ERP Automation – The need of the Business hour
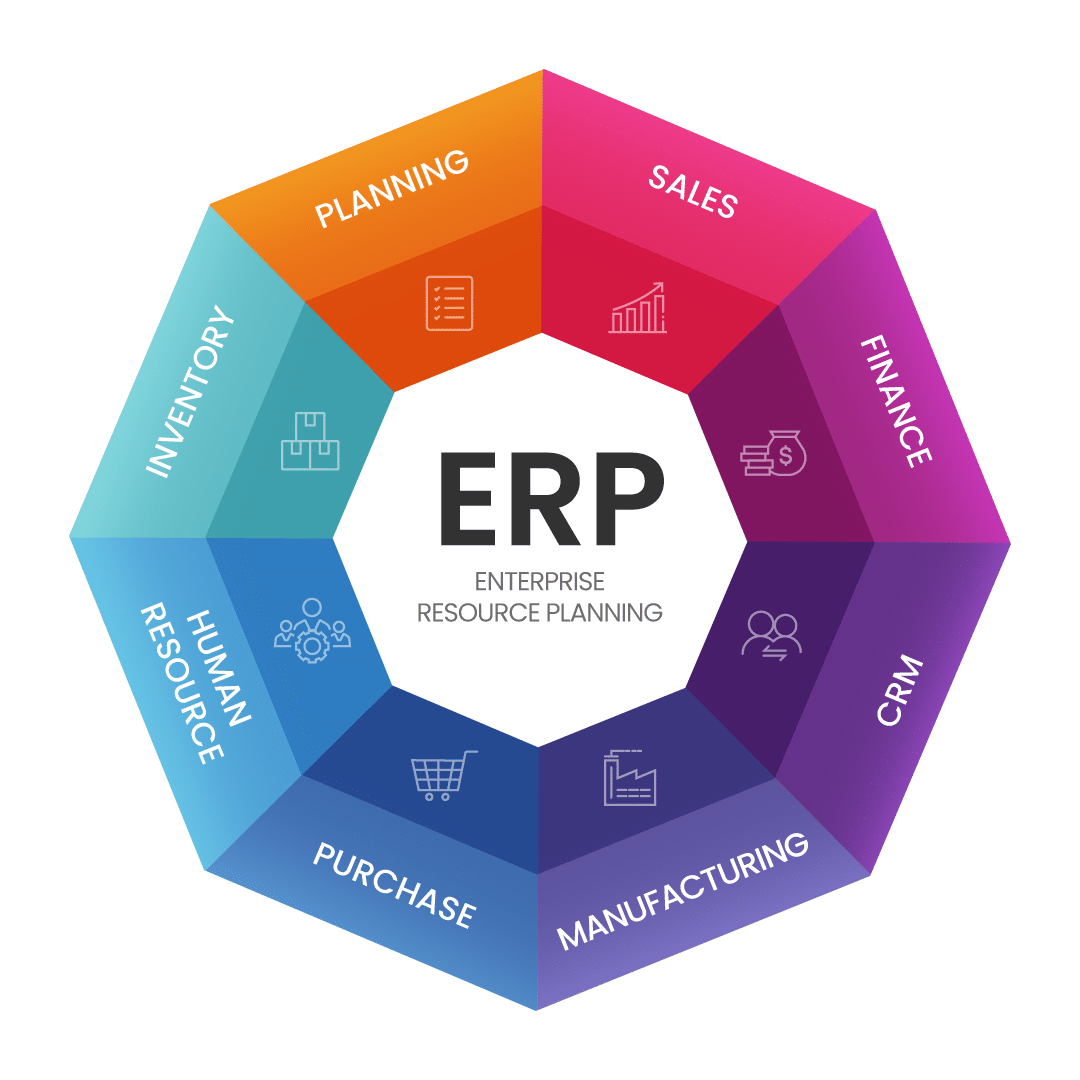
In modern business management, accurate and accessible data is crucial for success. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, which integrate business functions through centralized databases, have evolved from simple integration tools to automation powerhouses. As businesses face increasing complexity, the capabilities of ERP systems have expanded significantly. Today, ERP systems handle repetitive tasks efficiently and leverage predictive analytics to enable real-time, data-driven decision-making. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global ERP market is expected to grow from $54.76 billion in 2022 to $123.41 billion by 2030, indicating a robust demand for these systems. Notably, 95% of businesses report improved processes after adopting ERP systems, with an average ROI of 52%—highlighting their impact on cost savings and operational efficiency.
ERP automation relies on several key components, such as Intelligent Automation, which combines AI, ML, RPA, and business process management (BPM) to streamline business operations. It enhances predictive capabilities, allowing businesses to effectively anticipate needs and trends. Additionally, the Internet of Things (IoT) facilitates the integration of smart devices, enabling real-time data collection that significantly improves decision-making. A recent survey showing that 64% of companies now seek SaaS-based ERP solutions, hosted in the cloud, offering users the advantage of accessing applications from anywhere, promoting greater flexibility and collaboration among teams. The Cloud-Based ERP reduces paperwork and enhances data accessibility. Moreover, the emergence of multi-tier ERP systems facilitates connections with technologies such as warehouse management and digital marketing platforms, further driving operational efficiency.
ERP Automation Key Use cases:
Automated Data Entry:
This functionality automates the input of data such as sales orders, invoices, and inventory records, reducing the reliance on manual entry. By eliminating manual data entry, organizations can significantly speed up processing times, minimize errors, and free up staff to focus on more strategic tasks. This is ideal for businesses with high volumes of transactions that require fast and accurate data processing. Retailers handling thousands of transactions daily can benefit immensely from automated data entry, which allows them to manage inventory levels accurately and process orders swiftly.
Real-Time Reporting:
This feature generates reports on financial, sales, and operational metrics automatically, providing insights as soon as data is available. Organizations can make informed decisions quickly, allowing them to react to market changes and performance trends in real-time. This is particularly beneficial for management teams that need up-to-the-minute information to guide their strategies. Financial institutions can utilize real-time reporting to monitor cash flow, assess risk, and make investment decisions rapidly. For example, if a sudden economic shift occurs, real-time reporting allows a bank to adjust its investment strategies on the fly.
Financial Process Automation:
Automating processes like payroll, accounts payable, and receivable reduces the need for manual oversight. This leads to faster processing times and improved accuracy, ensuring that financial transactions are handled efficiently. This is suitable for organizations looking to streamline their finance departments and reduce administrative burdens. Hospitals can automate payroll processing for staff, ensuring timely payments and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Supply Chain Management:
ERP automation enhances various supply chain functions, including procurement, demand forecasting, and order fulfilment. Improved visibility and coordination across the supply chain can lead to cost reductions, better inventory management, and enhanced customer satisfaction. This use case is particularly relevant for manufacturing and retail companies that depend heavily on efficient supply chain operations. Manufacturers can enhance their procurement processes, reducing lead times and costs by automating order placements.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
Automating CRM tasks allows for better management of customer interactions, lead tracking, and marketing efforts. Enhanced customer engagement and service can lead to improved customer retention and increased sales. This is essential for businesses in customer-centric industries that prioritize relationship management. Online retailers can use automated CRM systems to manage customer interactions and tailor marketing strategies based on purchasing behavior. Another sector is Telecom companies who can automate customer support processes, enhancing response times and satisfaction.
Data Synchronization:
This functionality ensures that data across all ERP modules is consistent and accurate in real-time. It facilitates better collaboration and decision-making across departments, as everyone has access to the same information. This is crucial for organizations that rely on cross-departmental collaboration and accurate data sharing. Logistics companies can maintain up-to-date shipment tracking information across their systems, improving operational coordination.
Compliance Management:
Automating compliance management helps organizations generate regulatory reports and maintain adherence to industry standards automatically. Reduces the risk of non-compliance and potential fines while ensuring that all necessary documentation is readily available. This is particularly important for businesses in heavily regulated industries. Banks and financial institutions can automate compliance reporting to adhere to regulations such as AML (Anti-Money Laundering) and KYC (Know Your Customer).
Alerts and Notifications:
This feature sets up automatic alerts for critical business events, such as low inventory levels or pending approvals. Enables proactive management by notifying relevant stakeholders about important issues before they escalate. This is useful for operations managers who need to stay ahead of potential bottlenecks in processes. Manufacturers can receive alerts for equipment maintenance needs, preventing unexpected downtime and production delays.
The impact of ERP automation goes beyond theory, as evidenced by real-world implementations. Let’s explore how businesses across various industries have successfully leveraged ERP systems to drive operational efficiency. Here are a few of our Customer Success Stories that highlight the expertise and impact of 10xDS in ERP automation.
- Streamlined Bank Reconciliation: A large conglomerate in Kuwait organization digitized its cash application process in Oracle JD Edwards, processing 100 entries in under 30 minutes. (Case Study Link)
- Budget Transfer Automation: A power and utility company based in Saudi Arabia streamlined its request and approval processes with minimal manual intervention in Oracle and SAP systems. (Case Study Link)
- Vessel Procurement Automation: A diversified maritime and logistics company in Middle East automated the end-to-end procurement process using ShipNet One ERP, enhancing operational efficiency. (Case Study Link)
- Revenue Leakage Identification: A telecom company automated the detection of mismatches between ERP and billing modules, reducing errors and preventing revenue loss.
Considerations Before Starting ERP Automation
Embarking on ERP automation presents challenges that, while significant, are often outweighed by the substantial benefits. Organizations should be prepared for a high initial investment in licensing, hardware, and training, which typically leads to long-term savings and enhanced efficiency. The complexity of customization needed to align the ERP system with specific operational needs requires considerable effort but ultimately enhances functionality. Additionally, employee resistance during the transition from manual processes to automation can be mitigated through effective training and change management, fostering a more engaged workforce and smoother adoption. When managed thoughtfully, these challenges can pave the way for improved organizational performance and a strong return on investment. While ERP automation requires an upfront investment and thoughtful customization, the long-term benefits—enhanced efficiency, accuracy, and savings—far outweigh these challenges. With the right strategic partner, such as 10xDS, organizations can overcome these hurdles and realize strong returns on investment.
Conclusion
ERP automation is no longer optional for businesses looking to stay competitive. Beyond operational efficiency, these systems ensure compliance, accuracy, and improved decision-making. If your organization is yet to begin its digital transformation journey, now is the time. At 10XDS, our experts are ready to guide you in enhancing your operations through cutting-edge ERP solutions tailored to your needs. Connect with us today to start driving tangible business results.


