Polyfunctional Robots: The new definition of Versatility in Automation
As industries increasingly embrace automation, polyfunctional robots are emerging as a key innovation. Recognized as one of the top technology trends for 2025 by Gartner, these advanced machines transform human-machine collaboration by offering unparalleled versatility across sectors.
Understanding Polyfunctional Robots
Polyfunctional robots can perform multiple tasks, adapting in real time. Unlike traditional robots built for one job, they combine AI, sensors, modular hardware, and smart software to switch tasks seamlessly, boosting efficiency and productivity.
The key features of a polyfunctional robot include adaptability, achieved through AI-based decision-making, real-time learning, and sensor-driven adjustments, allowing the robot to respond dynamically to different tasks. Interoperability is ensured through cloud computing, API integration, and IoT connectivity, enabling seamless communication with other systems and devices. Scalability is supported by modular hardware, AI-driven upgrades, and robotic swarms, allowing these robots to evolve with changing operational demands and integrate effortlessly into diverse environments.
Technology behind Polyfunctional Robots
1. Multi-Modal Perception & Environment Sensing
Polyfunctional robots rely on advanced perception systems to understand their surroundings and make real-time decisions. These include:
- Computer Vision (CV): Uses cameras, LiDAR, and depth sensors to recognize objects, read QR codes, and detect obstacles.
- Proximity & Tactile Sensors: Enable safe interaction with humans and objects by measuring distance and force applied.
- Infrared (IR) & Ultrasonic Sensors: Assist in navigation and movement, especially in low-light environments.
- Edge Computing: Processes sensor data locally for real-time response, reducing latency.
We can relate this in an automotive factory, where a robot with a CV-powered robotic arm can switch between assembling parts, quality inspection, and material handling based on real-time sensor inputs.
2. AI-Driven Decision Making & Task Adaptability
- Machine Learning (ML): Robots analyze historical data to optimize task execution.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Enables communication with human operators and other machines.
- Reinforcement Learning: Helps robots improve task efficiency by learning from repeated actions.
- Real-Time AI Model Deployment: Uses cloud or edge-based AI inference to adjust operations dynamically.
For example, a warehouse robot equipped with AI and ML algorithms can decide whether to pick, place, scan, or transport packages based on weight, size, and order priority.
3. Modular Hardware & Dynamic Task Switching
- Interchangeable End Effectors: Robotic arms equipped with swappable tools (e.g., grippers, welding torches, suction cups) allow switching between assembly, welding, and painting.
- Self-Reconfiguring Components: AI-driven robotic modules can physically rearrange themselves based on task requirements.
- Collaborative Robotics (Cobots): Designed for safe human-robot interaction, adjusting force and speed based on human proximity.
In agriculture, a polyfunctional robot can switch between soil analysis, irrigation, and harvesting by swapping its sensor module for a robotic arm.
4. System Interoperability & Multi-Platform Integration
- Industrial IoT (IIoT): Enables real-time data exchange between robots, machinery, and enterprise systems.
- API & Cloud Integration: Robots can be programmed remotely and share analytics via cloud platforms.
- Digital Twins: A virtual simulation of the robot and its environment allows predictive adjustments before real-world execution.
- Communication Protocols: Uses OPC-UA, MQTT, and ROS (Robot Operating System) for seamless integration with industrial automation frameworks.
This is how a retail robot can sync with an inventory management system through API calls, identifying low-stock items and restocking shelves autonomously.
5. Autonomous Navigation & Motion Planning
- Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM): Allows robots to create real-time maps of their environment while navigating efficiently.
- Path Optimization Algorithms: Uses AI-powered route planning to minimize movement and reduce energy consumption.
- Actuator & Motion Control: Advanced robotic actuators adjust movement based on force feedback for precision tasks.
An autonomous logistics robot in a fulfilment centre uses SLAM to navigate aisles, avoiding obstacles and choosing the shortest path for package delivery.
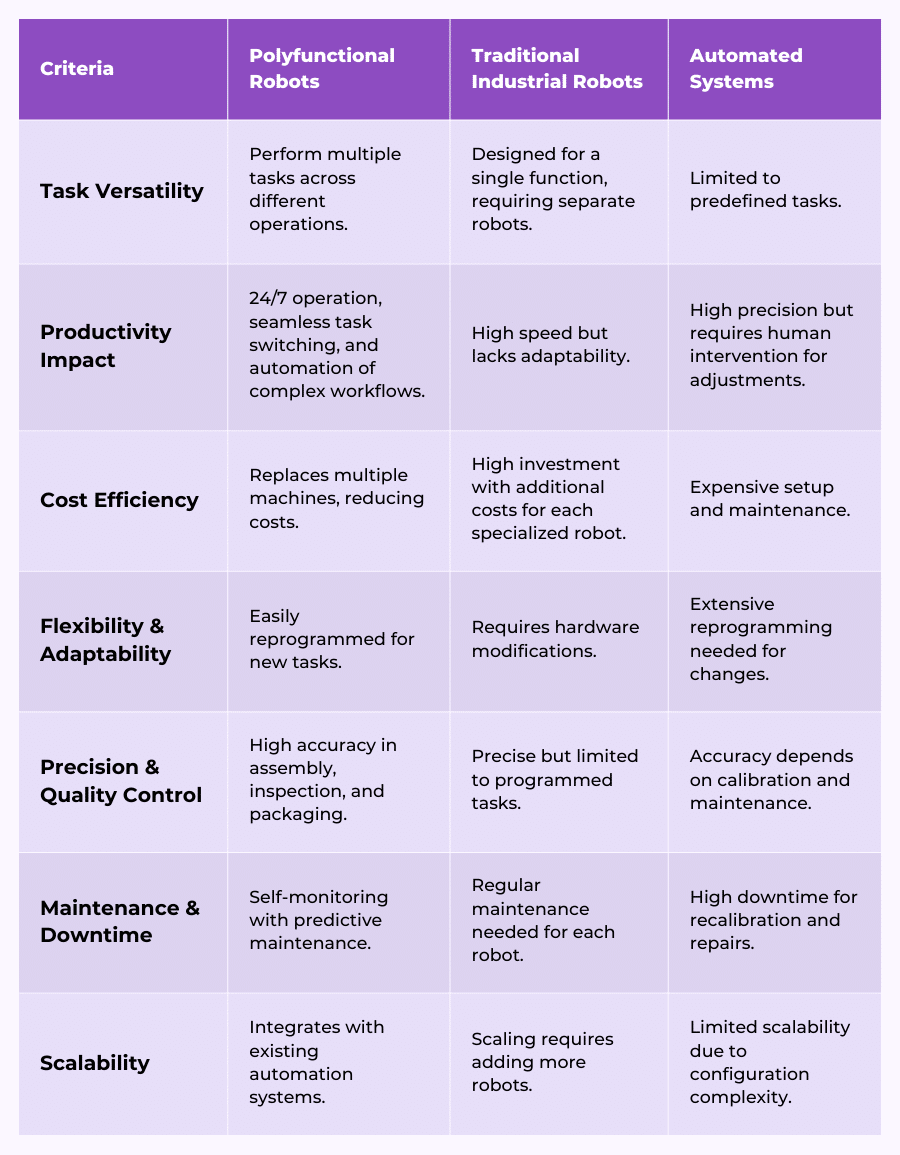
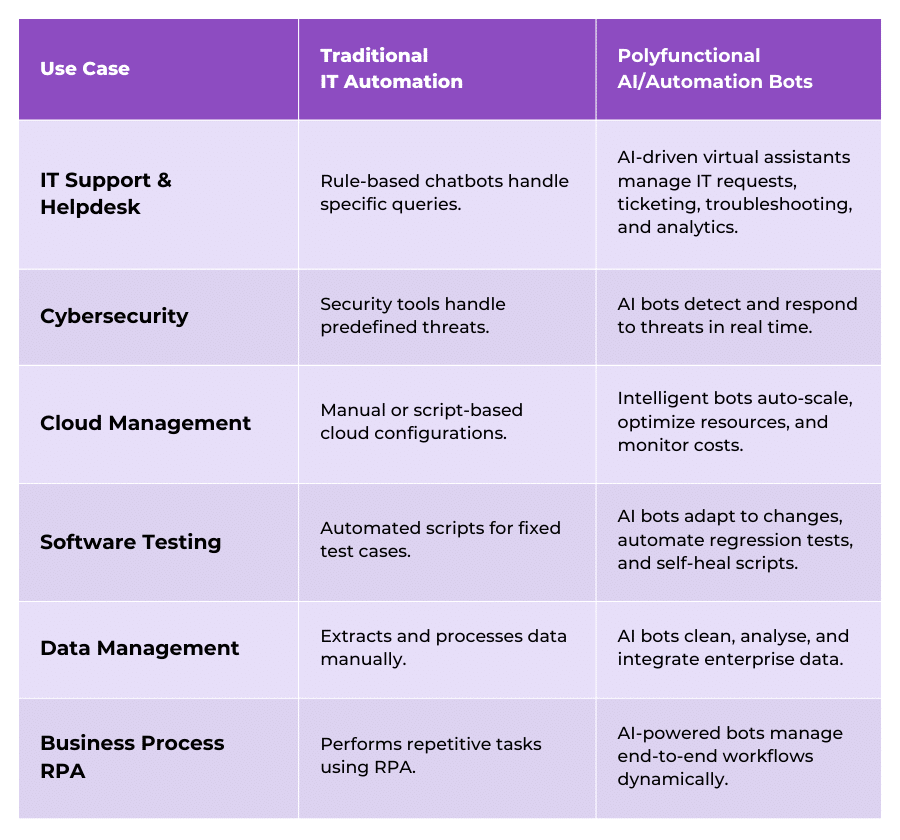
Comparison: Polyfunctional Robots vs. Traditional Automation
The following table provides a comparative overview of Polyfunctional Robots vs traditional automation, highlighting key differences across various operational aspects.
Industry-Wise Applications and Case Studies
1. Manufacturing – Automotive Assembly Line
In the automotive industry, polyfunctional robots handle welding, painting, and assembly. A single robot can transition between tasks like welding car frames, applying coatings, and assembling parts. This enhances production speed, lowers operational costs, and reduces machine redundancy.
2. Healthcare – Surgical Assistance
In healthcare, polyfunctional robots assist in minimally invasive surgeries, diagnostics, and patient care. Robots like da Vinci Surgical Systems improve precision and reduce human error, leading to better patient outcomes and faster recovery times.
3. Logistics & Warehousing – Automated Sorting & Packaging
Companies like Amazon and FedEx use polyfunctional robots to sort packages, package items, and prepare shipments. By handling multiple tasks within the supply chain, these robots optimize efficiency and reduce dependence on manual labour.
4. Agriculture – Crop Management
Agri-Bots automate seeding, watering, pest control, and harvesting. For example, John Deere’s AI-powered robots can plant seeds, analyze soil health, and apply fertilizers in a single workflow, improving efficiency and sustainability in farming.
5. Defence & Surveillance – Military Operations
In defence, robots are deployed for reconnaissance, bomb disposal, and search-and-rescue. A single robot can switch from surveillance mode to explosive neutralization, reducing risk to human personnel and enhancing mission effectiveness.
Polyfunctional Bots in IT Industry
In IT services, polyfunctionality applies through AI-driven automation and intelligent bots rather than physical robots. These bots handle diverse IT functions, reducing manual effort and improving efficiency.
Challenges and Considerations
While polyfunctional robots provide significant advantages, organizations must also consider certain challenges. The initial investment can be high, requiring substantial costs for acquisition and setup. Additionally, implementing these robots demands skilled personnel for programming, maintenance, and troubleshooting, which may necessitate specialized training. Furthermore, automation can impact the workforce by displacing human workers, making reskilling strategies essential to ensure a smooth transition and workforce adaptability.
Addressing Key Concerns
After exploring the topic, several important questions may arise. Below, we address some of the most common concerns to provide further clarity and insights.
Are Polyfunctional Robots Suitable for Small Businesses?
Although the initial investment may be high, small businesses can benefit significantly from polyfunctional robots by reducing labour costs and increasing operational efficiency. A restaurant, for instance, can use a single robot to greet customers, take orders, and clean tables. Similarly, a small warehouse can deploy robots to manage stock, pack shipments, and assist human workers, allowing businesses to scale without hiring additional staff. Over time, the cost savings and efficiency gains justify the initial expense.
What Are the Maintenance Requirements for These Robots?
To ensure longevity and efficiency, polyfunctional robots require regular maintenance, including software updates, sensor recalibrations, and mechanical servicing. Businesses using robotic arms in assembly lines conduct routine diagnostics to prevent downtime. AI-powered robots also undergo performance monitoring, where predictive maintenance tools analyse data to detect potential failures before they occur. Companies adopting these strategies significantly reduce unexpected breakdowns and ensure consistent operations.
How Do Businesses Integrate Polyfunctional Robots into Existing Operations?
Successful integration requires assessing current workflows, identifying automation opportunities, and training staff to work alongside robots. A logistics company, for instance, might deploy autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) to move inventory while human workers focus on sorting and quality checks. Businesses also invest in AI-driven platforms that enable robots to communicate with existing ERP systems, ensuring a smooth transition. The gradual implementation of these technologies ensures minimal disruption and maximizes benefits.
What Are the Cost Implications of Adopting Polyfunctional Robots?
While the upfront costs of acquiring and deploying robots can be substantial, the return on investment (ROI) often outweighs initial expenses. Companies save on labor costs, reduce errors, and boost efficiency, leading to long-term financial gains. A study by Gartner suggests that businesses investing in robotics experience a 20-30% increase in operational efficiency within the first few years. Additionally, leasing options and robotics-as-a-service (RaaS) models allow businesses to adopt this technology without significant capital investment.
What Is the Future of Polyfunctional Robots?
The future of polyfunctional robots is deeply intertwined with advancements in AI, 5G connectivity, and IoT integration. As machine learning evolves, these robots will become even more autonomous, capable of self-learning and adapting to new environments. Emerging technologies like humanoid robots are also gaining traction, with companies like Tesla and Boston Dynamics developing robots that mimic human movements for tasks like caregiving and home assistance. In the coming years, polyfunctional robots will further bridge the gap between human-machine collaboration, leading to more intelligent, efficient, and adaptive workforces.
Future Outlook
As AI and machine learning continue to evolve, polyfunctional robots will become increasingly sophisticated, enabling them to understand and interact with their environments more dynamically. Future trends in this field include greater autonomy, where robots can make real-time decisions based on AI-driven analysis, reducing the need for human intervention. Additionally, cost reductions will facilitate wider adoption among small and medium enterprises (SMEs), allowing them to leverage polyfunctional robotics for enhanced efficiency and scalability. Furthermore, the integration of robots into hybrid work environments will strengthen human-robot collaboration, optimizing workflows and improving overall productivity.
The Road Ahead
Polyfunctional robots are revolutionizing industries by enabling smarter workflows, minimizing operational costs, and enhancing precision. Their ability to seamlessly transition between tasks makes them invaluable across various sectors, including manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, and IT. By integrating AI-driven decision-making, modular hardware, and real-time adaptability, these robots improve efficiency, reduce downtime, and optimize resource utilization.
Are you looking for tailored automation solutions? Let’s explore how polyfunctional robotics can transform your industry and drive innovation! Talk to our experts now.